
Step 1 – Check that that your Router is on and connected.
Step 2 – Check that your PC / Laptop is connected to your router.
Step 3 – Check that your machine can communicate with your router.
Step 4 – Check that your machine can communicate with the internet.
Step 5 – Check that your machine can resolve internet addresses.
Step 6 – Report outage to ISP so they can get a technician on it.
Step 1 – Check that that your Router is on and connected.
The first thing to check is if your router is on, and is able to connect to the internet. As there are many kinds of routers and internet connection technologies (DSL, Fibre, LTE), you will have to refer to your routers manual for the appropriate indicator lights to check and their meanings. If you are using your cellular phone as a hotspot, a simple check if the phone is on and if you can browse the internet on your phone should suffice.
If your router is not powering on at all – you’ll need to replace your router.
If the router / phone has no connectivity – try giving it a reboot and then re-check. If you still have no connectivity, skip to Step 6.
Step 2 – Check that your PC / Laptop is connected to your router.
If Step 1’s tests look good, the next thing to check is if your PC / Laptop is actually connected to your router hotspot. Most people will use Wifi to connect to their router, but you can also connect via a LAN cable.

Ethernet cable – connectors.
If you are connecting via a cable like the one above, check that it is plugged in on your PC and on your router. Secondly, on the router – check that the indicator light for the port you are plugged in to is lit or flashing (the ports on router are usually numbered, 1,2,3,4 etc… with a corresponding light on the front).
If the indicator light for the port is not active, then try a different port on the router. If the result is the same, the following things could be wrong:
- The Ethernet cable is damaged, try a different cable.
- Your network card on your PC is damaged, replace the network card.
- Your router’s Ethernet ports are fried. Replace the router.
If the indicator lights indicate you’re connected – skip to step 3.
If you are connecting via WiFi, First check that you are connected to the router.
Windows 10
 This connection is connected, and windows believes it has a working internet connection. |  This connection is connected, and windows has no internet connection. This connection is connected, and windows has no internet connection. |
Windows 8.1 & 8
 This connection is connected, and windows believes it has a working internet connection. This connection is connected, and windows believes it has a working internet connection. |  This connection is connected, and windows has no internet connection. This connection is connected, and windows has no internet connection. |
Windows 7
 This connection is connected, and windows believes it has a working internet connection. This connection is connected, and windows believes it has a working internet connection. |  This connection is connected, and windows has no internet connection. |
If not, connect to your network. If you are connected / are able to connect – skip to step 3.
If windows fails to connect to the network – there is an issue on your PC with the wireless device – most likely a driver issue or a protocol issue.
Let’s first reset the TCP/IP stack and check if that resolves the issue.
Click on start, and type cmd. On the search item that comes up (cmd or command prompt), right-click and click on Run as Administrator – Click Allow/Yes if you get a User Account Control Prompt.
A window like this will pop up:
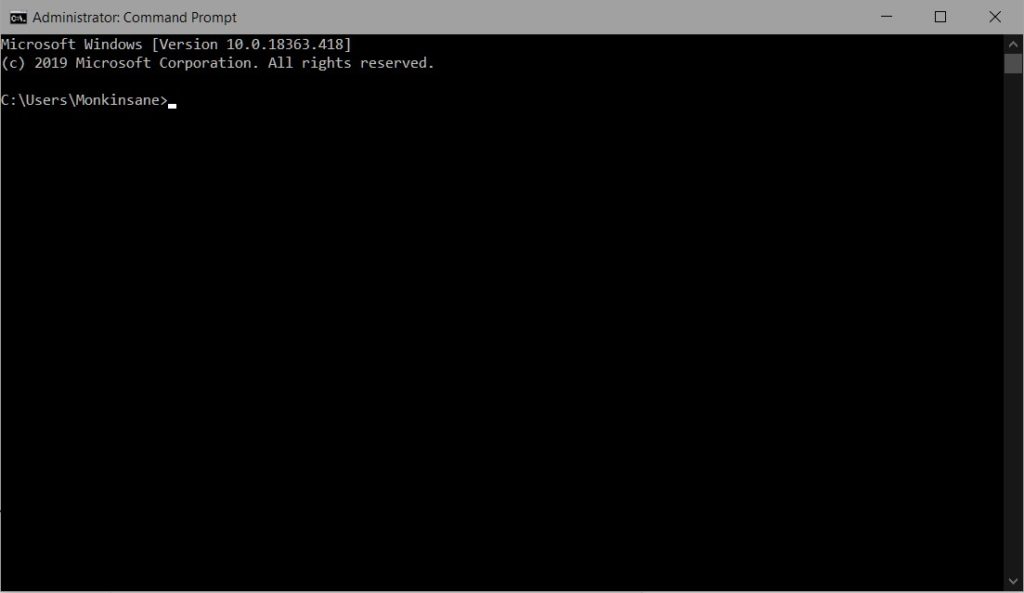
Type the following command in there and press Enter:
netsh winsock reset
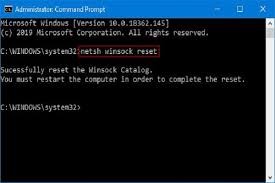
Reboot your computer & try to connect to the network again.
If that fails, let’s re-install the driver.
Press the Windows Key + X and click on device manager on the menu that pops up.
In device manager, Drop down the Network Devices menu and find your Wireless card. Take a note of the device name – you may need to download drivers again.

Right Click on the device, and click on uninstall device.
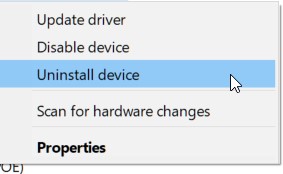
A confirmation dialog will pop up – do not tick the “Delete the driver software…..” option and click on Uninstall.

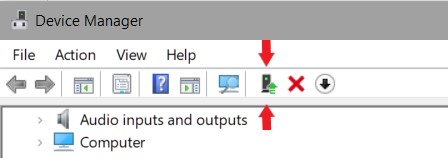
Once done, in the main “Device Manager” window, click on the icon indicated by the screenshot below. This will scan your computer for any hardware that does not appear on the current list of hardware (our newly uninstalled wireless card), and install the drivers for it again. Once that process is done – try and connect to your wireless network again – you will get prompted for your network password again.
If that fails you will need to download the drivers for your wireless card, from the internet and install them again from the provider’s installation package. If you still cannot connect after that – you will need to contact an IT Technician to look at the problem for you.
Step 3 – Check that your machine can communicate with your router.
Once you’ve established that you’re physically connected to your router (either by cable or Wi-Fi), you need to check whether your PC can actually talk to your router.
There are some circumstances which may cause you to be connected to router but unable to communicate.
For Example:
- PC Failed to get an ip address from your router.
- Corrupted TCP Stack on windows.
- Firewall Blocking the connection.
First off, lets check if your PC received an IP address from your router.
Right-Click on the network status icon in the notification tray, and click on “Open network & internet settings”.
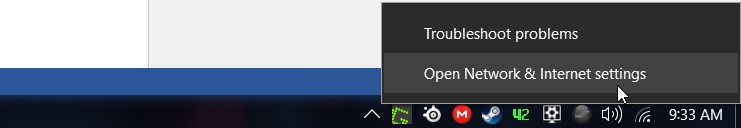
On the Status page, click on Network and Sharing Center.
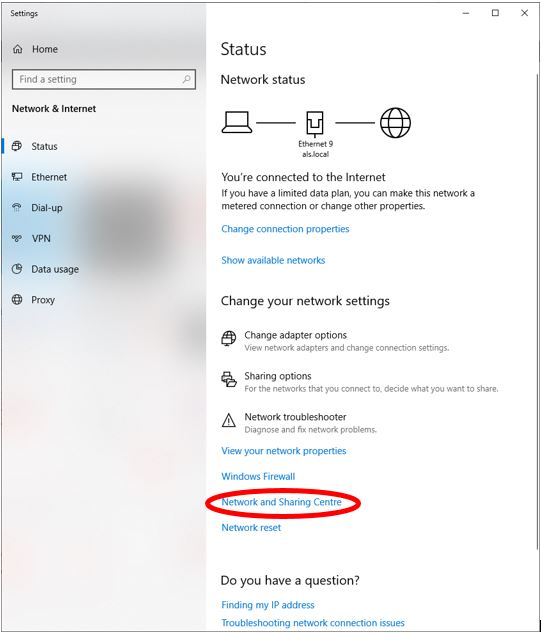
In Network & sharing Center, click on your connection’s name.
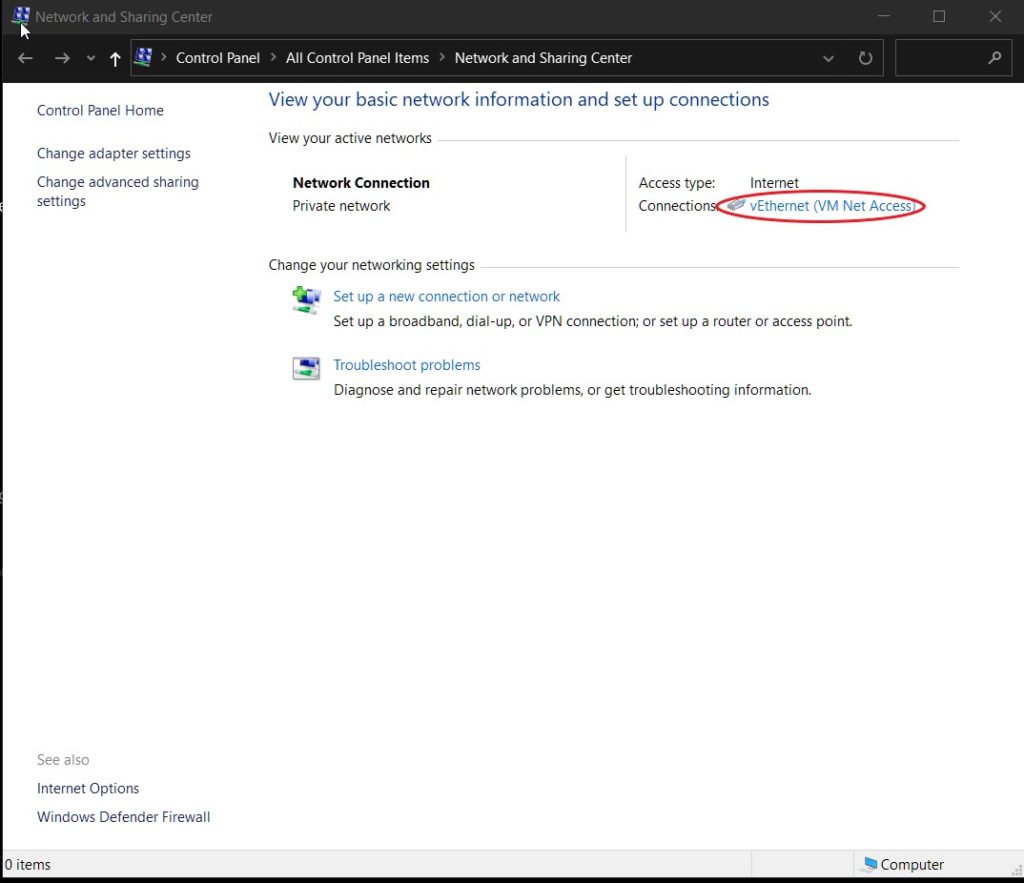
Next, Click the Detail button on the windows that pops up.
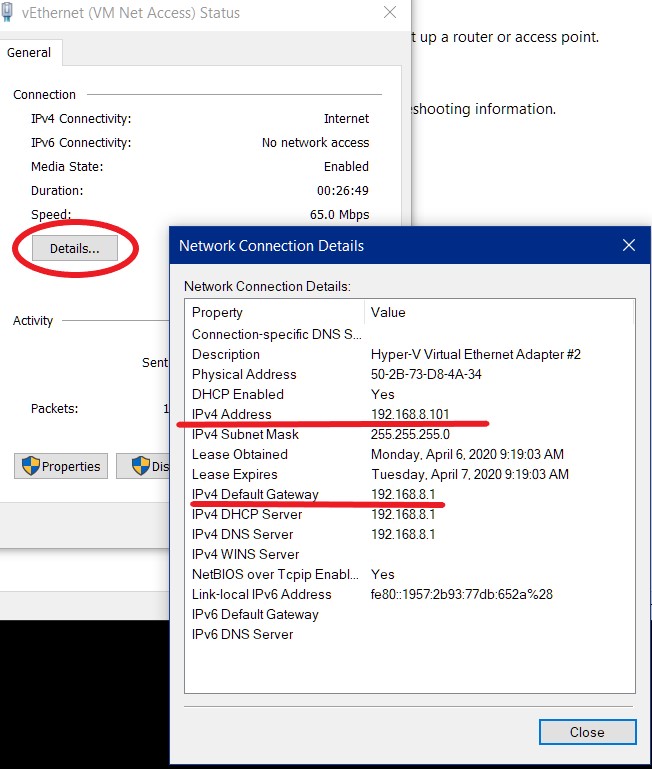
On the Network Connection Details page, if you have an IPv4 Address that starts with 169.254 then your machine did not get an IP from your router. Power cycle your router and check again once it is booted. If you still get the 169.254 address, contact an IT professional to assist you.
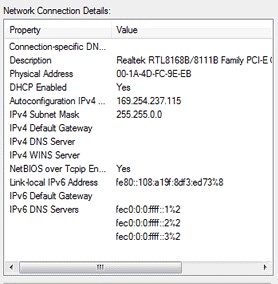
If however you get a different IP range (in the example case: 192.168.8.101), your machine did get an IP from your router. Take note of the IPv4 Default Gateway address, this is the IP address of your router. Next we need to ensure that we can actually talk to the router, Click on start, and type cmd. On the search item that comes up (cmd or command prompt), right-click and click on Run as Administrator – Click Allow/Yes if you get a User Account Control Prompt.
In the Command Prompt window, type ping <IP OF ROUTER>
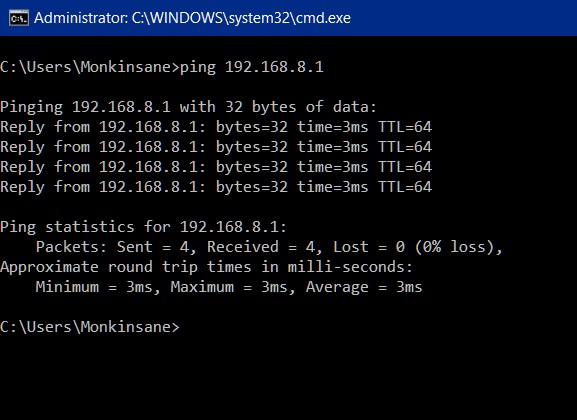
If you get anything other than what you see in the example (Reply from <ROUTER IP>), your PC is unable to actually talk to the router, contact an IT Professional to assist you. If your output looks similar to the above picture, your PC can talk to your router.
Step 4 – Check that your machine can communicate with the internet.
Next you need to check whether your machine can actually “talk” to the internet. We do this by pinging an internet address. Open a command prompt again if it’s not still open and type ping 8.8.8.8. If all is well you’ll see a response like the one below:
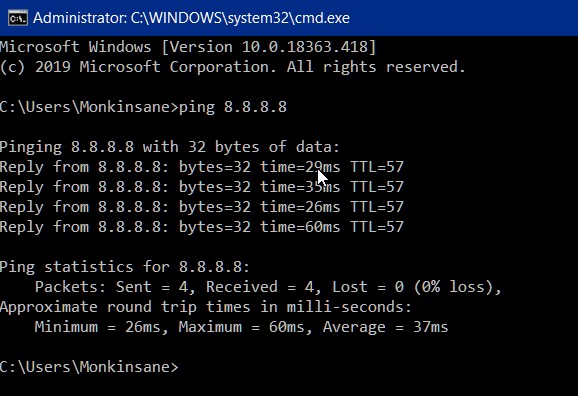
If you get “destination host unreachable” – or any other message other than the above, your router is either not connected to the internet or is unable to connect/communicate with the internet.
To check on your router’s connection status, check the connection light on it as described in step 1. (see your router’s manual for which light indicates an internet connection). If that shows as connected – you’ve most likely got a ISP issue. Connect another device to your router, and check if that device can access the internet to verify. Then contact your ISP and report the issue. If your other device can access the internet, you’ve got an issue with either your hardware, drivers or operating system. Contact an IT professional to assist.
Step 5 – Check that your machine can resolve internet addresses.
Each website on the internet has an IP address. When you go to www.google.com for example, your machine contacts a DNS server and asks it “what is www.google.com’s IP address?”. This server then responds with the machine’s ip address, and your browser then connects to that IP address and loads the webpage.
It sometimes happens that for whichever reason (the dns server your router uses by default is down etc….), that your machine & router, while still connected to the internet, cannot resolve site addresses. If this is the case – it’s a relatively simple fix.
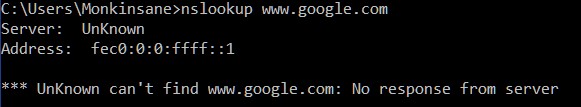
First check if your machine can resolve dns addresses to ip addresses by typing the following into a command prompt window: nslookup www.google.com .
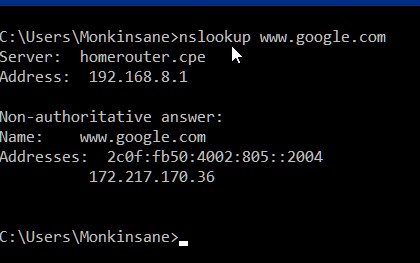
If you get a response like the above, and are still unable to browse the internet, contact an IT Professional to assist. If however you get a response like the one below (anything but the response above really), you can tell your machine to use a different DNS server than the one assigned by your router. (server: will have your router’s ip, not unknown)
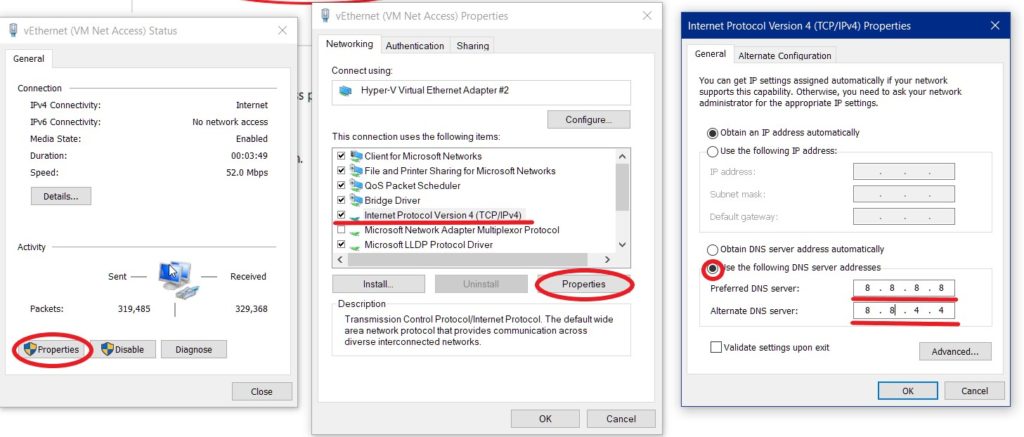
Right-Click on the network status icon in the notification tray, and click on “Open network & internet settings”.

On the Status page, click on Network and Sharing Center.

In Network & sharing Center, click on your connection’s name.

On the Next dialog that opens up(left in the image below), Click on Properties. The middle window below will open up. On that window, select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”, and click on Properties. The Right Window will open up. Select and fill in everything as indicated on that right window in the image below, and click on OK, then on OK again on the previous window. Close everthing but the Command Prompt window.
Now that you’ve set a different DNS server, repeat the nslookup tests at the start of this section, check if you can browse the internet. If not, you’ve got an underlying issue on your PC, and will need to contact an IT professional for assistance.
Step 6 – Report outage to ISP so they can get a technician on it.
At this point, your only recourse is to contact your ISP – as you’ve ruled out a local issue on your end. Report your internet problems, and hopefully they’ll resolve the issue quickly.

[…] TeamViewer is a great program to get able to get remote assistance when you are out of your depth and need a helping hand. It allows another party to access your desktop as if they were sitting in front of it. This mean that so long as you have an internet connection you can get assistance (if you have an issue with your internet check out the Internet Troubleshooting Guide). […]